The Private Equity is defined as the investment activity in the venture capital in unlisted companies. Transactions are usually supported by funds that acquire a minority or majority stake in an SME.
But how does a Private Equity Fund evaluate an SME and based on what it invests? What are the indexes you analyze? What are the differences between a company that is financed and one that is not financed?
In this article we will explain in detail what are the indices and parameters that the PE funds analyze before investing in a project.
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL INDICES
- Leverage Ratio (ie the debt ratios of companies in relation to their earnings, in private equity continue to rise)
- Gearing Ratio (ie the debt ratio as a measure of financial leverage that demonstrates the degree to which a company’s operations are financed by equity with respect to creditors’ financing)
- Debt Service Ratio (ie the total debt service ratio is a measure of debt service that lenders use as a rule of thumb to determine the percentage of gross income that is already spent)
- Interest Coverage Ratio (ie the interest coverage ratio is both a debt ratio and a profitability index used to determine the ease with which a company can pay interest on its outstanding debt. The interest coverage rate can be calculated dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) during a given period with payments of the company’s interests due within the same period)
SME STRATEGIC ANALYSIS
- 5 Porter’s forces: this is the model that analyzes the competitive forces with which the company finds itself having to deal. These are direct competitors, suppliers, customers, potential new entrants to the market and substitute goods producers
- Sector analysis: definition, attractiveness, structure, market size, growth, plants, capital intensity, cyclicality and seasonality and regulations
ASSESSMENT METHODS
- Pricing benchmark
- Unit costs
- SWOT Analysis
- Profitability indexes
- Rotation indexes
- Profitability indexes
- Shareholding and Management of SMEs
- Financial analysis
- Business Plan with three scenarios: management houses, banking houses and accounting
INDEX OBSERVED
Table 1
| PRIVATE EQUITY | PRIVATE DEBT |
| IRR % | Ability to repay the debt |
| Valuation of the quotas | Sensitivity Analsysis |
ANALYSIS FOR INDICES
- Liquid assets
- External market factors
- Solvency
PRE-MONEY COMPANY ASSESSMENT OF A PE / PD
- No DCF
- No TV
- Yes Multiples Method
COMPANY STRUCTURE DURING A PE OPERATION
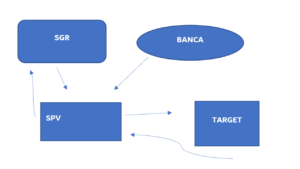
ENTRY PROCEDURE BY A PRIVATE EQUITY FUND
Table 2
| CAPITAL INCREASE | ACQUISITION OF THE QUOTAS |
| Minority transactions | Majority operations |
| Buy Out | Leveraged Buy Out |
Only after a careful analysis, therefore, can the private equity fund decide to invest in the company shares of the target company and monetize, at the end of the fixed period, the investment.
The BizPlace Team